Trusted Certificates
Liam Sharp
Posted 24 July, 2023 by Liam Sharp in
Trusted Certificates
File > Settings > Trusted Certificates (Windows, Linux)
Screaming Frog SEO Spider > Settings > Trusted Certificates (macOS)
A Man In The Middle (MITM) proxy will resign TLS certificates. If a resigned certificate is not from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), the TLS connection will be rejected.

Companies employing this style of proxy will usually distribute an X.509 certificate to employees. This X.509 certificate can be used by the SEO Spider by adding it to a ‘Trusted Certificates Folder’.
The SEO Spider will only accept X.509 certificates with the following extensions: .crt, .pem, .cer and .der.
How To Add A Trusted Certificate
When a proxy is changing the issuer of a certificate, it can be quickly seen within Screaming Frog. Click ‘File > Settings > Trusted Certificates’ on Windows or ‘Screaming Frog SEO Spider > Settings > Trusted Certificates’ on macOS and then click the ‘Discover’ button.

The genuine issuer for the Screaming Frog website certificate is ‘GTS CA 1P5’, however, you should see this is as something different – such as your proxy, for example ZScaler or McAfee. This shows the issuer of the certificate is being changed in your networking environment.
If you are seeing ‘ZScaler, McAfee’ etc as the issuer certificate, then click the ‘Add’ button next to it.

This will add the certificate file to the SEO Spider trusted certificates trust store.
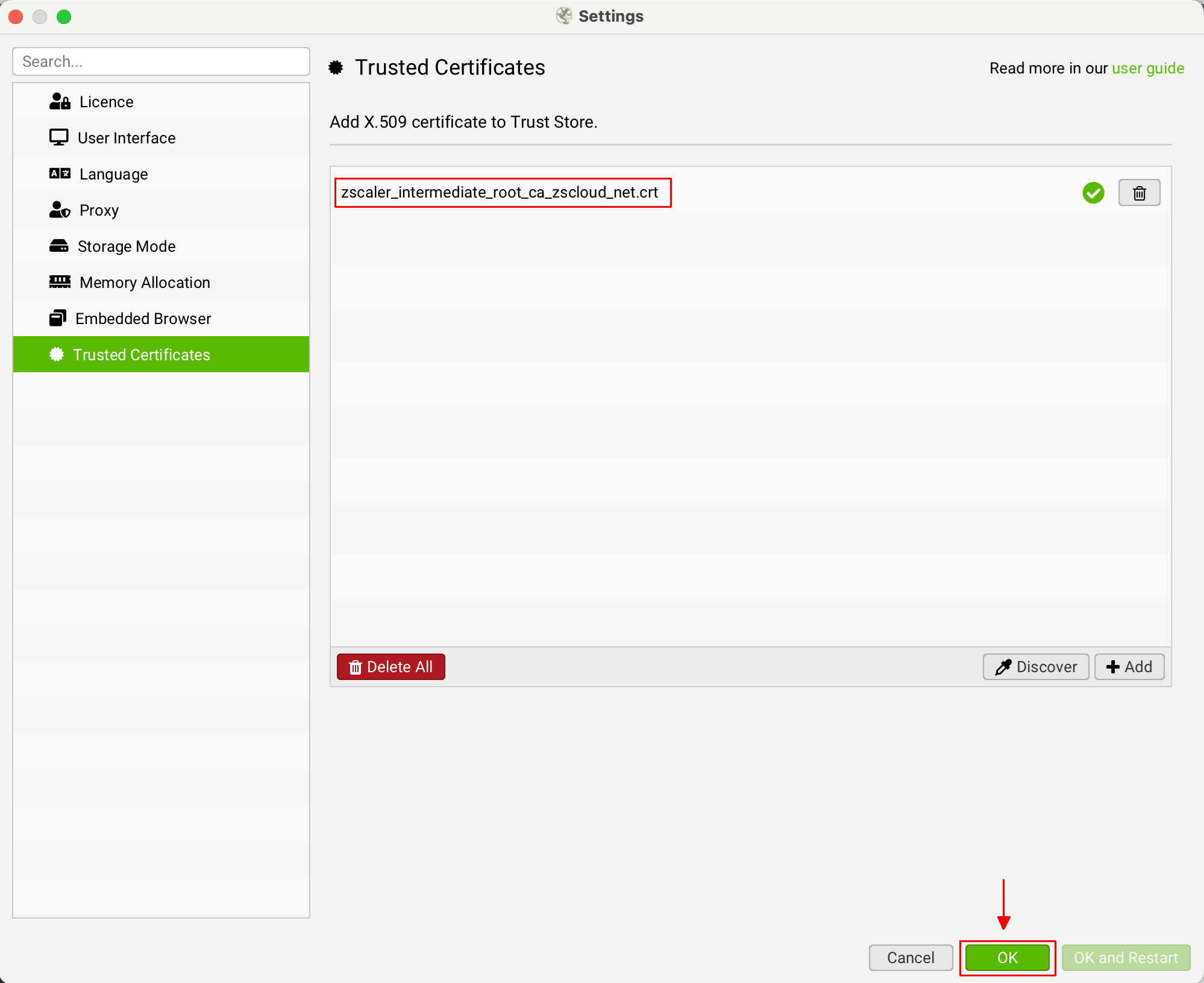
You can then click ‘OK’. You should then be able to validate your licence.






